THE ENERGY NEEDS OF ATHLETES
Our diet provides us with energy for our activities and allows us to maintain our body mass and our physiological functions. The energy balance is the difference between what is absorbed (food and drink) and what is spent (vital functions and physical activities). If our calorie consumption is greater than what we burn, there is an imbalance which results in weight gain (and this does not matter the nature of the food absorbed in excess, you can get fat with an apple!). Whether we want to lose weight or gain it, we must keep in mind the essential balance between our energy and structural needs.
THE CALCULATION TO DETERMINE THE APPROPRIATE INTAKE DEPENDS ON SEVERAL VARIABLE FACTORS
- The basal metabolic rate (MB) (determined according to its weight, sex, height and age); it corresponds to the energy expended by the body at rest to maintain vital functions (breathing, digesting, sleeping
- Physical activity level (PAL)
Adequate dietary intake (= the Daily Energy Expenditure – DEJ –) corresponds to the MB x NAP calculation ; it must be distributed equitably throughout the day, taking into account the times and durations of training.
HOW TO CALCULATE YOUR BASAL METABOLISM
In France, we usually use Black & al's formulas depending on the gender of the person:
![]()
With P=weight kg / T=height in m / A=age in years
It is then necessary to evaluate and calculate the NAP. For this, all the activities of the athlete's day must be listed and timed. Each duration of activity will then be multiplied by one of the corresponding coefficients established by ANSES*:
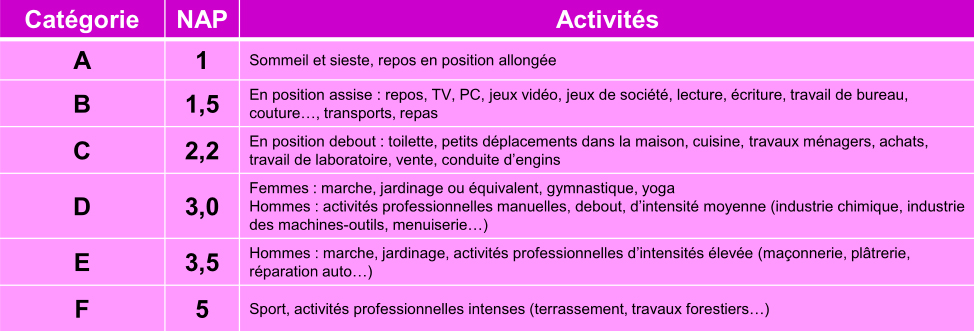
EXAMPLE FOR A 35-YEAR-OLD WOMAN WEIGHING 53 KG FOR 1,65 M:
Example of Sophie, sporty but with a very sedentary professional activity (Black & al formula for a woman)
-
Basic metabolism MB = 0,963x53^0,48x1,65^0,5x35^-0,13 = 5,239 MJ i.e. 5239 kJ ➔ 1250 Kcal
-
Assessment of physical activity level NAP = to be discussed with your dietitian
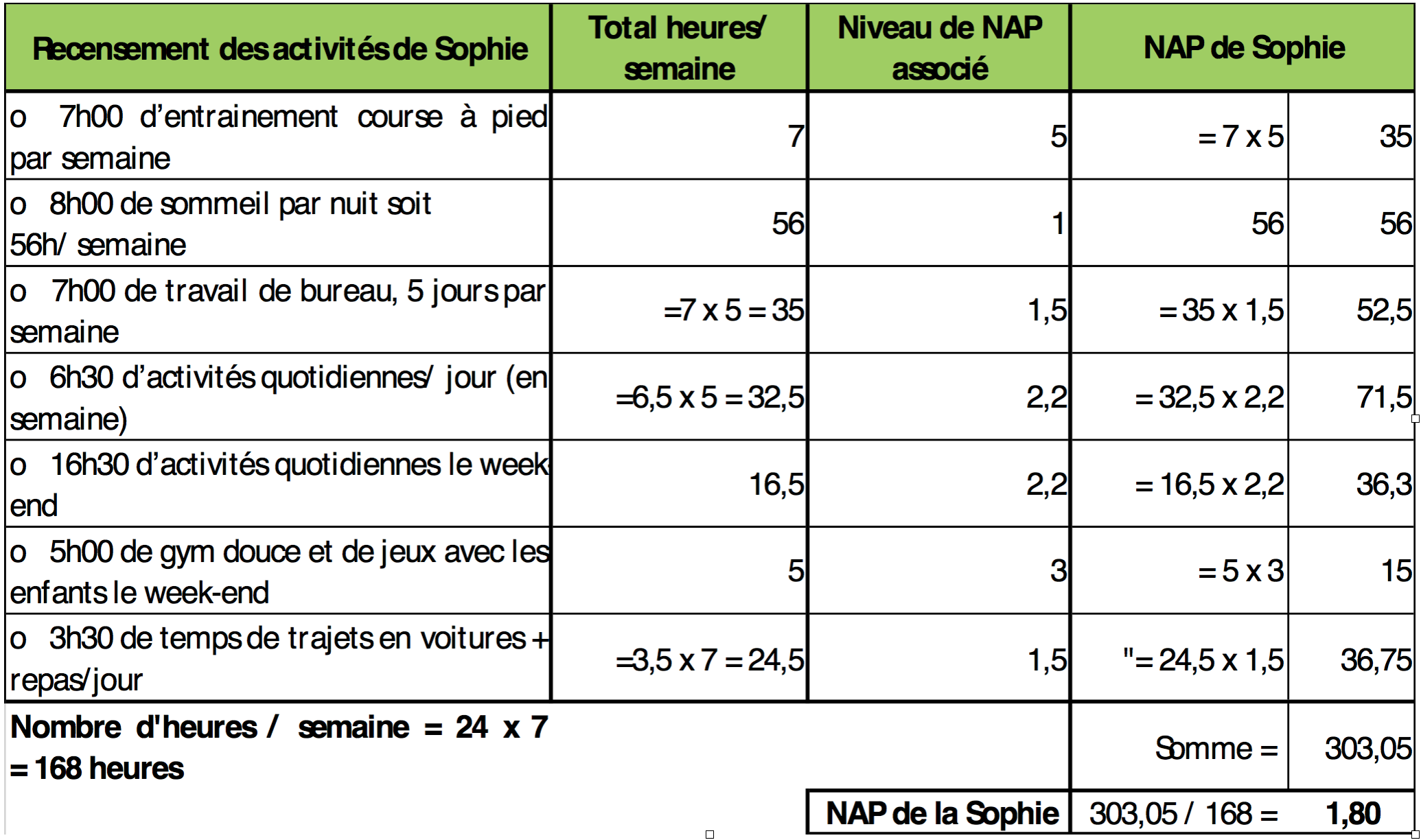
The calculated MB and the obtained NAP make it possible to calculate the Daily Energy Expenditure (ALREADY):
LAST = 1250 Kcal x 1,8 = 2250 Kcal
Thus, the daily ration should be 2250 kcal with 15% in proteins, 35% in lipids and 50% in carbohydrates (essentially complex), for its health, its performance and the maintenance of its staturo-weight balance.
EXAMPLE OF CORRESPONDING MENUS ON A DAY:
Breakfast :
1 yaourt
2 slices of country bread
10 g butter
1 tbsp jam or honey
Lunch :
1 bowl of lemon cumin grated carrots
1 tbsp rapeseed oil
1 grilled chicken fillet with herbs
5 tbsp white rice
½ plate of sautéed zucchini
garlic with 1 tbsp olive oil
30 g of cheese
1 small slice of country bread
1 fresh seasonal fruit
Snack:
15 unsalted almonds
1 fresh seasonal fruit
Having dinner :
1 small bowl of quinoa salad (onion, parsley…)
with 1 tbsp of chickpeas +
1 soft-boiled egg
1 small slice of country bread
½ plate of oven-roasted butternut squash
with herbs with 1 tbsp olive oil
1 yaourt
Article written for our partner Atlet by:
Caroline JOUCLA • State-certified nutritionist-dietician • www.carolinejoucladieteticienne.com
ATLET-COLLECTION
You may also be interested in these articles:
-
Sandra Marianacci explains to us what naturopathy is!
-
SPORT AND PROTIDES in partnership with ATLET
-
Carbohydrates: How much daily, by Guillaume Klein

